georeference: Geolocation R package
If you are working with places mentioned in historical or literary texts, you may want to geolocate them using digital gazetteers.
I wanted to automate the process —as the geocode() function from the ggmap package does with the Google API—, but using Pelagios instead, a gazetteer more suitable for historical and literary texts. So, directly based on the geocode() function, I wrote an R package with just one function that returns latitude, longitude, location name, url/id, and searched query from the gazetteers Pelagios (default), Geonames, and Wikipedia (georeferenced articles stored in the GeoNames database).
The georeference R package is available in my Github repository. Examples of usage:
# load the library
library(georeference)
# run the function
georef("Rome")
# output
lon lat name url searched_name
1 12.4843 41.8926 Roma http://pleiades.stoa.org/places/423025 Rome
# run the function
# GeoNames requires a user account (free) to use their API services.
georef(c("Valladolid", "Complutum"), source = "geonames", inject = "username=your_geoname_username")
# output
lon lat name searched_name geonameid
1 -4.72372 41.65518 Valladolid Valladolid http://sws.geonames.org/3106672
2 -3.35996 40.48205 Alcalá de Henares Complutum http://sws.geonames.org/3130616
georeference & leaflet for R
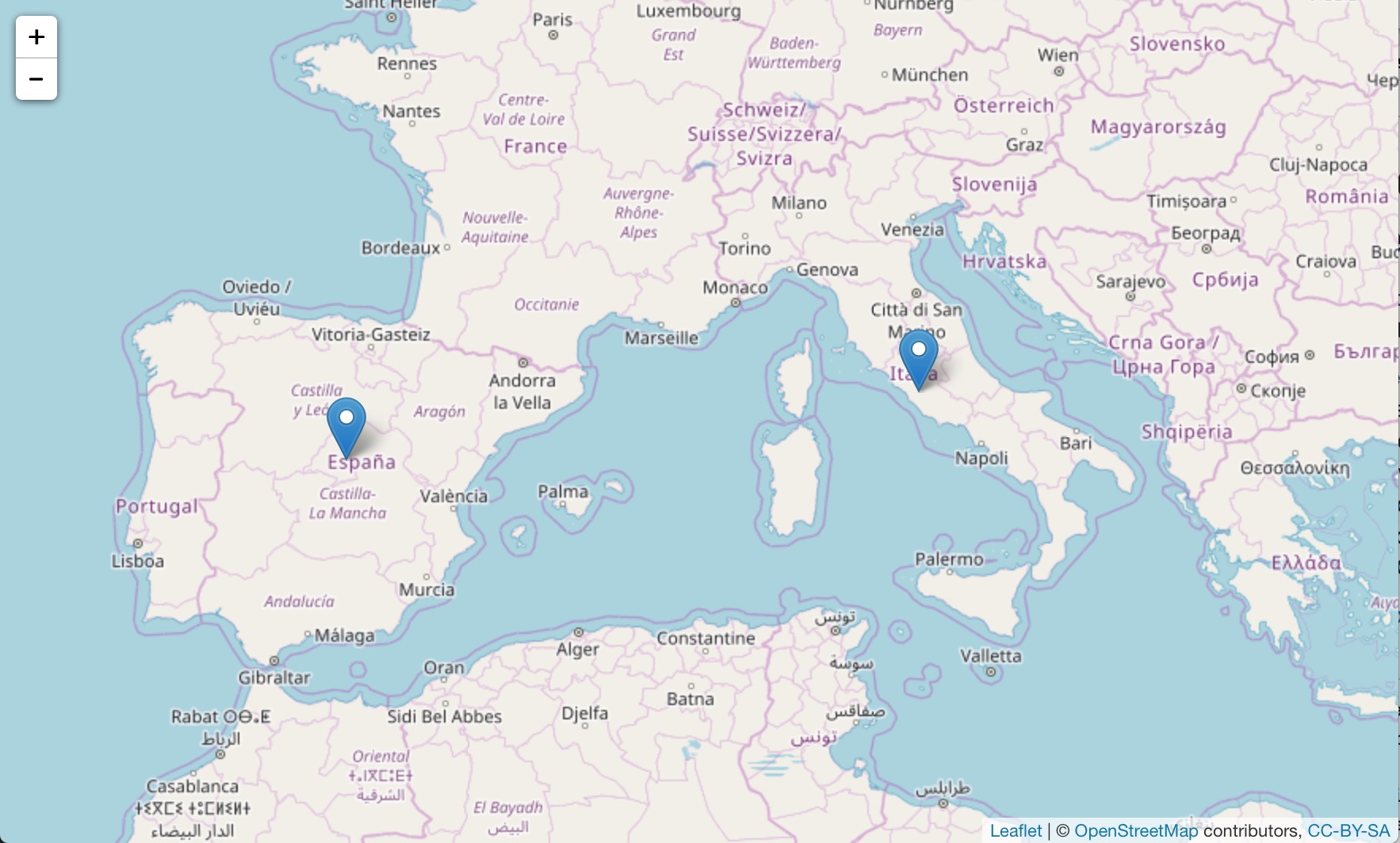
Once you have latitude and longitude, and without leaving the R environment, it is relatively easy to put the places on a interactive web map using the leaflet package for R:
# load the libraries
library(georeference)
library(leaflet)
# run the georef function
places = georef(c("Rome", "Complutum"))
# run the leaflet functions
leaflet() %>%
addTiles() %>%
addMarkers(places$lon, places$lat)